Monday, August 8, 2011
Saturday, July 2, 2011
Alcohols
Origin of the word alcohol:
Of those, ethanol (C2H5OH) is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, and in common speech the word alcohol refers specifically to ethanol.The word alcohol appears in English in the 16th century, loaned via French from medical Latin, ultimately from the Arabic الكحل (al-kuḥl, "the kohl, a powder used as an eyeliner").The current Arabic name for alcohol is الكحول al-kuḥūl, re-introduced from western usage.
The general formula of alcohol is CnH2n+1OH. An alcohol is any organic compound in which a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) is bound to a carbon atom, usually connected to other carbon or hydrogen atoms.
![]()
Of those, ethanol (C2H5OH) is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, and in common speech the word alcohol refers specifically to ethanol.The word alcohol appears in English in the 16th century, loaned via French from medical Latin, ultimately from the Arabic الكحل (al-kuḥl, "the kohl, a powder used as an eyeliner").The current Arabic name for alcohol is الكحول al-kuḥūl, re-introduced from western usage.
The general formula of alcohol is CnH2n+1OH. An alcohol is any organic compound in which a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) is bound to a carbon atom, usually connected to other carbon or hydrogen atoms.
The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority.
Common Alcohols :
The most commonly used alcohol is ethanol, C2H5OH. Ethanol has been produced and consumed by humans for millennia, in the form of fermented and distilled alcoholic beverages. It is a clear flammable liquid that boils at 78.4 °C, which is used as an industrial solvent, car fuel, and raw material in the chemical industry. Ethanol in this form is known generally as denatured alcohol; when methanol is used, it may be referred to as methylated spirits or "surgical spirits".
The simplest alcohol is methanol, CH3OH, which was formerly obtained by the distillation of wood and, therefore, is called "wood alcohol". It is a clear liquid resembling ethanol in smell and properties, with a slightly lower boiling point (64.7 °C), and is used mainly as a solvent, fuel, and raw material. Unlike ethanol, methanol is extremely toxic: One sip (as little as 10 ml) can cause permanent blindness by destruction of the optic nerve and 30 ml (one fluid ounce) is potentially fatal.Two other alcohols whose uses are relatively widespread (though not so much as those of methanol and ethanol) are propanol and butanol. Like ethanol, they can be produced by fermentation processes. Etymology:
![]() Because of hydrogen bonding, alcohols tend to have higher boiling points than comparable hydrocarbons and ethers. The boiling point of the alcohol ethanol is 78.29 °C, compared to 69 °C for the hydrocarbon Hexane (a common constituent of gasoline), and 34.6 °C for Diethyl ether.
Because of hydrogen bonding, alcohols tend to have higher boiling points than comparable hydrocarbons and ethers. The boiling point of the alcohol ethanol is 78.29 °C, compared to 69 °C for the hydrocarbon Hexane (a common constituent of gasoline), and 34.6 °C for Diethyl ether.
Alcohols, like water, can show either acidic or basic properties at the O-H group. With a pKa of around 16-19, they are, in general, slightly weaker acids than water, but they are still able to react with strong bases such as sodium hydride or reactive metals such as sodium. The salts that result are called alkoxides, with the general formula RO- M+.
Meanwhile, the oxygen atom has lone pairs of nonbonded electrons that render it weakly basic in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric acid. Mild oxidation in the presence of oxygen gives the products below :
[] |
Thursday, June 23, 2011
Aspirin
Turns to be the Century Miracle Drug!
Aspirin Description:
Uses of Aspirin:
Aspirin is used to relieve many kinds of minor aches and pains--headaches, toothaches , muscle pain, menstrual cramps, the joint pain from arthritis, and aches associated with colds and flu. Some people take aspirin daily to reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other heart problems. Many other over-the-counter medicine contain Aspirin. Alka-Seltzer Original Effervescent Antacid Pain Reliever, for example, contains aspirin for pain relief and sodium bicarbonate to relieve acid indigestion, heartburn, and sour stomach.Aspirin, also known as 'acetylsalicylic acid', has a chemical formula of C9H8O4.
Aspirin is prepared salicyilic acid according to the reaction below :
Tuesday, May 17, 2011
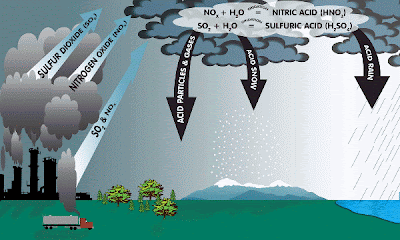
Acid Rain

Acid rain is a human-related phenomena. Since our industries are so fond of burning fossil fuels (coal and oil) they tend to release a lot of sulfur into the air. This sulfur combines with the oxygen already present in the air to form sulfur dioxide (SO2).
Also, since we like to drive big fancy cars rather than ride bikes or walk, we cause the formation of nitrogen oxides (NO or NO2 or NO 3, etc) in air from burning gasoline.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
Formation of SO2 and nitrogen oxides (NO & NOx): ![]()
S(in fuel) + O2 -------> SO2
N2 + O2 -------> 2NO
NO + .5O2 -----> NO2
Formation of hydrogen peroxide
N2 + O2 -------> 2NO
NO + .5O2 -----> NO2
Formation of hydrogen peroxide
VOC + sunlight + HO2 (in air) -------> H2O2
***VOC = Volatile Organic Compound ***
Formation of acids :
***VOC = Volatile Organic Compound ***
Formation of acids :
SO2 + H2O2 and O3 (in clouds) -------> H2SO4 SO2+ OH + O2 (in air) --------------> H2SO4
SO2 + Oxidants (from wet surfaces) --> H2SO4
NOx + sunlight + OH (air) ------------> HNO3
SO2 + Oxidants (from wet surfaces) --> H2SO4
NOx + sunlight + OH (air) ------------> HNO3
EFFECTS OF ACID RAIN
Also, the leaves of many plants and trees can be severely damaged by acidic precipitation. It is believed that acid rain leaches calcium and magnesium from the soil. This causes a decrease in the ratio of calcium to aluminum in the soil, which stimulates the uptake of aluminum by roots. The uptake of aluminum by trees and plants can be destructive. Finally, in cites and towns all over the world, stone structures, such as buildings, ancient ruins, etc are being deteriorated by the corrosive effects of acidic rainfall.

Wednesday, May 4, 2011
Autoionozation of water for Grade 10
The self-ionization of water (also autoionization of water, and autodissociation of water) is the chemical reaction in which a proton is transferred from one water molecule to another, in pure water or an aqueous solution, to create the two ions, hydronium, H3O+ and hydroxide, OH−.

Chemically pure water has an electrical conductivity of 0.055 µS·cm−1. According to the theories of Svante Arrhenius, this must be due to the presence of ions. The ions are produced by the self-ionization reaction
- H2O + H2O
H3O+ + OH−
This equilibrium applies to pure water and any aqueous solution.
The value of Kw decreases as temperature increases and it decreases with increasing pressure.
The equilibirum expression for the above reaction is written below and is treated mathematically like all equilibrium expressions.
If one knows the concentration of either the hydronium ions or of the hydroxide ions in a water solution,. the other ion concentration can be determined.
Example: What is the hydronium ion concentration in a water solution that is 0.050 M NaOH?
The NaOH is a strong base and will 100% dissociate into its component ions. Therefore, the concentration of the hydroxide ions will be 0.050 M. The hydronium ion concentration is then calculated.
The NaOH is a strong base and will 100% dissociate into its component ions. Therefore, the concentration of the hydroxide ions will be 0.050 M. The hydronium ion concentration is then calculated.
[H3O+] = (1 x 10-14)/(0.050) = 2.0 x 10-13 M
Example: What is the hydroxide ion concentration in a water solution that is 4.0 x 10-5 M H3O+?
Example: What is the hydroxide ion concentration in a water solution that is 4.0 x 10-5 M H3O+?
[OH-] = (1 x 10-14)/(4.0 x 10-5) = 2.5 x 10-10 M .
Sunday, April 24, 2011
Ozone Depletion
Ozone (O3) is found in two different parts of our atmosphere. Ground level ozone, a human health irritant and component of smog, is found in the lower atmosphere (troposphere) and has nothing to do with the "ozone hole." However, ozone in the stratosphere—the layer of atmosphere above the troposphere _ accounts for the vast majority of atmospheric ozone. Stratospheric ozone is protective for human health as it absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun, preventing the radiation from hitting Earth's surface and harming living organisms from this biologically dangerous radiation.

The stratospheric ozone layer shields life on Earth from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation. Chemicals that destroy ozone are formed by industrial and natural processes. With the exception of volcanic injection and aircraft exhaust, these chemicals are carried up into the stratosphere by strong upward-moving air currents in the tropics. Methane (CH4), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrous oxide (N2O) and water are injected into the stratosphere through towering tropical cumulus clouds. These compounds are broken down by the ultraviolet radiation in the stratosphere. Byproducts of the breakdown of these chemicals form “radicals”—such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and chlorine monoxide (ClO)—that play an active role in ozone destruction. Aerosols and clouds can accelerate ozone loss through reactions on cloud surfaces. Thus, volcanic clouds and polar stratospheric clouds can indirectly contribute to ozone loss.

.

Tuesday, April 19, 2011
Global Warming
Green house effect:
The greenhouse effect is the process by which absorption and emission of infrared radiation by gases in the atmosphere warm a planet's lower atmosphere and surface.Naturally occurring greenhouse gases have a mean warming effect of about 33 °C (59 °F).The major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect; carbon dioxide (CO2), which causes 9–26 percent; methane (CH4), which causes 4–9 percent; and ozone (O3), which causes 3–7 percent.

 Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation.
Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century and its projected continuation. Most of the observed temperature increase since the middle of the 20th century has been caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases, which result from human activities such as the burning of fossil fuel and deforestation.
Consequencies:An increase in global temperature will cause sea levels to rise and will change the amount and pattern of precipitation, probably including expansion of subtropical deserts.
Warming is expected to be strongest in the Arctic and would be associated with continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice.

Other likely effects of the warming include more frequent and intense precipitation events, extreme weather events, species extinctions due to shifting isotherms, and changes in agricultural yields.

Thursday, April 14, 2011
Balancing chemical reactions
- Identify each element found in the equation. The number of atoms of each type of atom must be the same on each side of the equation once it has been balanced.
- If possible, start with an element found in one compound on each side of the equation. Change the coefficients (the numbers in front of the compound or molecule) so that the number of atoms of the element is the same on each side of the equation. Remember! To balance an equation, you change the coefficients, not the subscripts in the formulas.
- Once you have balanced one element, do the same thing with another element. Proceed until all elements have been balanced. It's easiest to leave elements found in pure form for last.
- Check your work to make certain the charge on both sides of the equation is also balanced.
Example of Balancing a Chemical Equation
? CH4 + ? O2 → ? CO2 + ? H2OIdentify the elements in the equation: C, H, O
Identify the net charge: no net charge, which makes this one easy!
- H is found in CH4 and H2O, so it's a good starting element.
- You have 4 H in CH4 yet only 2 H in H2O, so you need to double the coeffient of H2O to balance H. 1 CH4 + ? O2 → ? CO2 + 2 H2O
- Looking at carbon, you can see that CH4 and CO2 must have the same coefficient. 1 CH4 + ? O2 → 1 CO2 + 2 H2O
- Finally, determine the O coefficient. You can see you need to double the O2 coefficient in order to get 4 O seen on the product side of the reaction. 1 CH4 + 2 O2 → 1 CO2 + 2 H2O
- Check your work. It's standard to drop a coefficient of 1, so the final balanced equation would be written: CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)